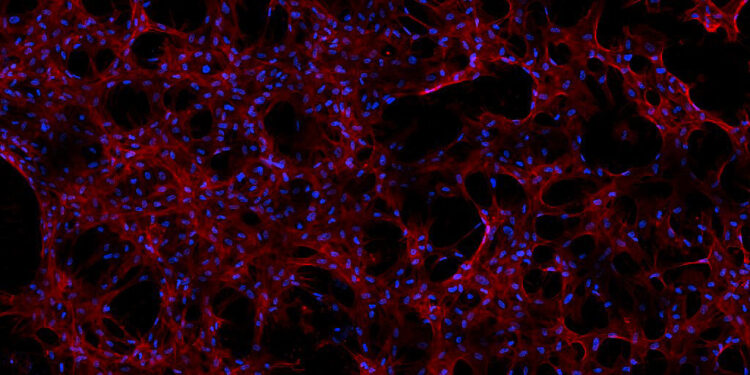
Spaceflight has been shown to affect cellular biology in numerous ways, providing valuable insights into how living organisms react to the environment of space. The International Space Station (ISS) serves as a unique laboratory for conducting biological research in microgravity.
Key Research Areas
Research conducted on the ISS has uncovered several critical areas that are impacted by spaceflight:
- Cell Growth and Development: The lack of gravity affects how cells grow and differentiate, providing information that could help develop new medications and therapies on Earth.
- Gene Expression: Spaceflight causes changes in gene expression profiles, which can inform us about how cells adapt to microgravity over time.
- Cellular Repair Mechanisms: Understanding how cells repair themselves in space can lead to new insights into combating degenerative diseases.
Microgravity Experiments
Microgravity experiments have played a significant role in uncovering these cellular behaviors. The ISS provides researchers with the ability to conduct long-term studies in an environment where gravity’s influence is minimal, offering a closer look at the cellular level processes.
Potential Benefits
The insights gained from these studies can have far-reaching benefits:
- Medical Advancements: Information from space-based cellular studies can contribute to the development of treatments for a variety of illnesses.
- Agricultural Improvements: Understanding plant cell reactions to microgravity could lead to more resilient crop strains.
- Enhanced Survival Strategies: Insights into cellular adaption may improve our strategies for long-duration space missions.
Overall, the impact of spaceflight on cellular biology is a field of exciting potential, leading us not only to breakthrough discoveries for space travel but also having profound implications for life on Earth.