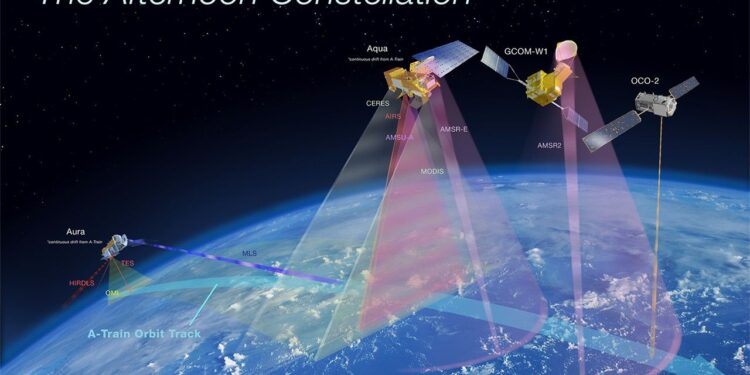
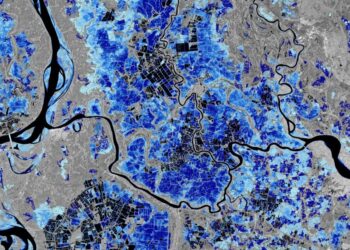
The past decade has been monumental for NASA’s OCO-2 (Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2) mission. Since its launch, OCO-2 has played a crucial role in providing high-quality data about Earth’s carbon cycle, greatly enhancing our understanding of how carbon dioxide sources and sinks are distributed across the globe.
Innovations and Achievements
One of the innovative aspects of OCO-2 is its precision in measuring atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. This satellite has an unparalleled ability to collect data with high spatial and temporal resolution, providing insights that were previously unattainable using ground-based methods.
Over the years, OCO-2 has contributed to major scientific advancements, including:
- The identification of regional carbon sources and sinks.
- Enhanced understanding of the role of plants and oceans in carbon absorption.
- Improved monitoring of the impact of human activities on the global carbon cycle.
Global Impact and Future Prospects
The OCO-2 mission has not only advanced scientific knowledge but has also influenced global carbon monitoring efforts, paving the way for policies aimed at mitigating climate change. The data from OCO-2 supports the efforts of various international climate agreements by providing evidence that can guide decision-making.
Looking ahead, the insights gained from OCO-2 will continue to inform strategies for managing Earth’s carbon budget effectively. The mission serves as a cornerstone for future satellite missions designed to further explore and monitor atmospheric changes.
For more information on the achievements and future prospects of NASA’s OCO-2 mission, kindly visit the NASA Science website.