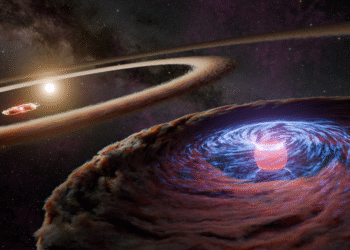
NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) has delivered groundbreaking insights into the behavior of black holes. This innovative space observatory, launched to study the X-ray emissions from cosmic sources, is offering new perspectives on how black holes interact with their environment.
Key Findings
Researchers have uncovered that IXPE’s measurements can pose challenges to current theories of black hole physics. By examining the polarization of X-ray light from black holes, scientists are able to gain critical information about the origins and properties of these enigmatic cosmic phenomena.
Among the important discoveries is the indication that many black holes have a “heartbeat,” with fluctuations in X-ray emission that echo characteristics more complicated than previously thought. These findings suggest a need to refine or reevaluate existing models of how black holes accrete matter and eject material.
Significance of IXPE’s Mission
The mission has underscored the importance of understanding high-energy astrophysical processes, potentially altering our comprehension of how black holes influence the galaxies in which they reside. These revelations are expected to influence how future observations and theoretical work are conducted.
Future Research Directions
The insights provided by IXPE have opened new avenues for research, prompting scientists to explore further into the behavior of other cosmic phenomena using polarimetry. As IXPE continues to monitor black holes and other X-ray emitting bodies in space, it promises to expand our understanding of the universe.
For more information, you can view the original article on NASA’s official site here.