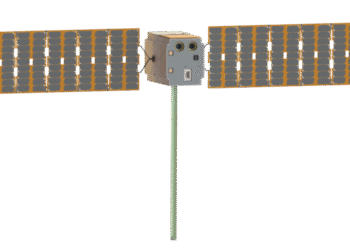
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite has achieved a significant milestone with the successful acquisition of a signal. This event marks a crucial step in the joint mission by NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) dedicated to Earth observation.
The achievement signifies the satellite’s capability to communicate effectively with ground systems, paving the way for important scientific data collection. The mission’s objective is to employ advanced radar technology to monitor subtle changes in Earth’s surface, providing valuable insights into phenomena such as earthquakes and changes in ice sheets.
Among the many benefits of the NISAR mission, its ability to enhance our understanding of Earth’s processes stands out. NISAR’s data will be crucial for researchers studying our planet’s complex environmental dynamics, such as land motions, vegetation, and the intricate interactions within ecosystems.
The satellite operates powerful L-band and S-band synthetic aperture radars. These radars allow for comprehensive and high-resolution imaging capabilities, crucial for observing our planet on a day-to-day basis, regardless of weather conditions.
As the mission progresses, the data collected will support a wide range of applications, including:
- Assessing risks associated with natural disasters like landslides and floods
- Monitoring agricultural patterns and drought conditions
- Tracking deforestation activities and land use changes
The successful signal acquisition by the NISAR satellite positions it as a significant tool for global monitoring and scientific exploration, promising to fill data gaps for various environmental studies and policy interventions.
For more detailed information on NISAR and its recent developments, you can visit the official blog post on the NASA Science website.