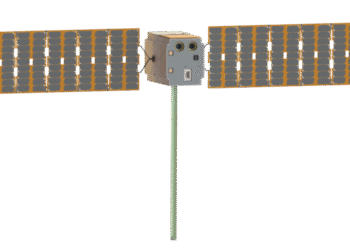
A newly developed satellite, the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR), has been launched to improve Earth observation capabilities. This satellite is a joint venture between the United States’ NASA and India’s ISRO, focusing primarily on tracking Earth’s changing surfaces and monitoring crucial climate change indicators.
Key Objectives of the NISAR Satellite
The NISAR satellite aims to provide detailed imagery to study the Earth’s ecosystems, surface changes, and natural hazards such as earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, and landslides. By utilizing advanced radar technology, it seeks to offer precise and consistent data regarding the dynamics of Earth’s surface. This information is vital to understanding various natural and human-induced processes and their impacts on the environment.
Technological Features and Contributions
- Sophisticated Radar Technology: NISAR is equipped with the most advanced dual-frequency radar currently available.
- Collaborative Engineering: It combines the expertise of NASA’s and ISRO’s scientists and engineers, enabling scientific breakthroughs and innovation.
- Rigorous Monitoring Capability: The satellite can monitor changes at fine temporal and spatial resolutions.
This collaborative mission signifies a major enhancement in our ability to predict and observe Earth processes, contributing significantly to scientific research and policy-making in the context of climate action and disaster preparedness.
For further details, explore the official NASA announcement.