The European Space Agency (ESA) has commenced the construction of the **LISA mission** (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna), which is an ambitious project aimed at detecting and measuring gravitational waves. These cosmic ripples in space-time are caused by some of the most **energetic processes** in the universe, such as merging black holes.
Significance of the LISA Mission
LISA is significant because it is designed to observe gravitational waves from space, complementing Earth-based detectors like LIGO and Virgo. This mission will enable scientists to explore the universe’s hidden aspects, potentially revealing unknown phenomena and **advancing our understanding** of cosmic events.
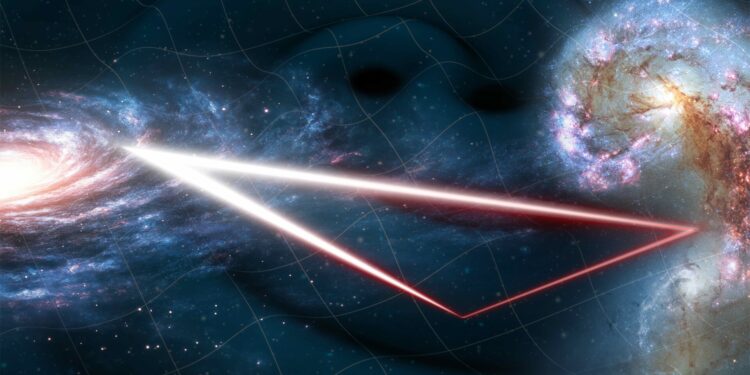
The LISA mission will consist of three spacecraft arranged in a triangular formation, following Earth’s orbit around the sun. These spacecraft will be capable of detecting minute changes in distance caused by passing gravitational waves, allowing for a catalog of ripple events through high-precision measurements.
Technical Aspects and Goals
- LISA will detect low-frequency gravitational waves, which are inaccessible to ground-based detectors due to Earth’s noise interference.
- The triangular spacecraft formation will have a vast separation of 2.5 million kilometers, allowing them to function as a giant interferometer in space.
- The mission will address fundamental questions concerning **stellar evolution**, galaxy formation, and the nature of black holes.
The development of the LISA mission is projected to take about a decade, with ambitions to launch the spacecraft in the 2030s. This marks a significant milestone in space exploration, as detecting gravitational waves from space will enhance the scope of astrophysical research.
Source: ESA – Construction of ESA’s ambitious LISA mission begins