“`html
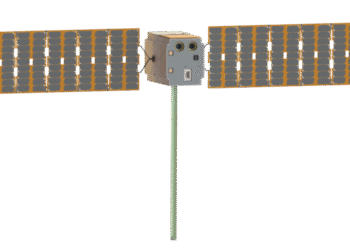
The **NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR)** mission has achieved a significant milestone by deploying its largest radar reflector antenna. This satellite is a collaborative effort by **NASA** and the **Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)**, designed to improve Earth observation capabilities. The reflector antenna, which spans about 39 feet in diameter, is essential for the satellite’s mission to study global environmental changes, including deforestation, glacial retreat, and natural disasters.
Significance of the Radar Antenna
The deployment of this large **antenna** marks a crucial phase in preparing the satellite for its upcoming Earth observation tasks. Large antennas like this are invaluable for gathering data at high resolution across vast areas, contributing vital information for climate scientists and researchers.
Benefits and Applications
The cutting-edge technology aboard the NISAR satellite will enable the monitoring of several environmental factors. Here are some of its notable applications:
- Tracking changes in the **earth’s crust**, which could help predict earthquakes.
- Measuring the current **rate of ice melt** in polar regions.
- Monitoring **ecosystems** to assess the global carbon cycle.
- Enhancing agricultural management by observing **crop yields** and land usage.
By combining resources and expertise, NASA and ISRO aim to create a more robust set of tools for addressing pressing environmental issues. The data gathered will be instrumental in environmental management and disaster response.
More information on this groundbreaking achievement can be found at the source.
“`